Polycarbonate injection molding has emerged as a vital process in various industries, offering a blend of strength, durability, and versatility in producing intricate designs. As the demand for high-quality polycarbonate products continues to rise, mastering the techniques involved in injection molding becomes crucial for manufacturers looking to stay competitive. Understanding the nuances of polycarbonate injection molding is essential, from selecting the right materials to optimizing processing parameters, ensuring that the final products meet stringent quality standards.
In this guide, we will explore ten essential tips that can significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of polycarbonate injection molding operations. By adhering to these strategies, manufacturers can minimize defects, reduce material wastage, and achieve consistent results. Whether you are new to the field or seeking to refine your existing processes, the insights shared here will serve as an invaluable resource in navigating the complexities of polycarbonate injection molding. Embracing these techniques can lead to improved product quality, increased production rates, and ultimately, greater customer satisfaction.

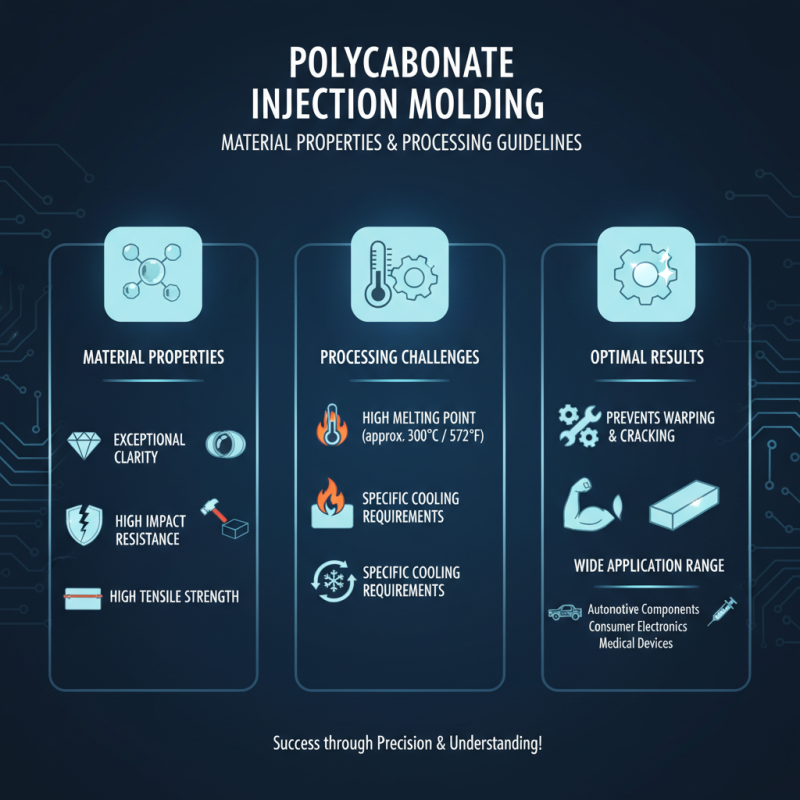
Understanding the material properties of polycarbonate is crucial for successful injection molding. Polycarbonate, known for its exceptional clarity and impact resistance, presents unique challenges and opportunities in the molding process. Its high tensile strength makes it an ideal choice for a variety of applications, from automotive components to consumer electronics. To achieve optimal results, processors must carefully consider processing temperatures and cooling times, as this material has a relatively high melting point and specific cooling requirements to prevent warping or cracking.
One essential tip for working with polycarbonate is to ensure that the mold design allows for efficient heat transfer. Utilizing conformal cooling channels can help maintain uniform temperatures throughout the mold, reducing cycle times and enhancing product quality. Additionally, implementing a gradual injection speed can mitigate flow-induced stresses, helping to maintain the integrity of the finished product.
Another important consideration is the selection of additives when formulating polycarbonate for injection molding. Incorporating materials such as UV stabilizers can improve the longevity of molded parts when exposed to sunlight. Moreover, controlling moisture content prior to processing is vital, as polycarbonate is hygroscopic and can absorb water, leading to defects such as splay and bubbles in the final product. By understanding the properties and behaviors of polycarbonate, and implementing these strategic tips, manufacturers can enhance their injection molding processes and achieve superior results.
Preparing your equipment for optimal polycarbonate injection molding is crucial to achieving high-quality production and efficiency. One of the foremost considerations is ensuring your injection molding machine is properly calibrated. A well-calibrated machine not only enhances precision during the injection process but also minimizes material waste.
According to a study by the Society of Plastics Engineers, optimal machine settings can reduce cycle times by up to 20%, translating to significant cost savings for manufacturers. Regular maintenance checks can prevent equipment malfunctions that might lead to expensive downtimes.
In addition to machine calibration, the importance of temperature control cannot be overstated. Polycarbonate, known for its high impact resistance and clarity, requires specific processing temperatures to retain its desirable properties. Research indicates that maintaining the melt temperature between 230°C to 270°C is essential for consistent quality. Deviating from this range can lead to issues such as discoloration or poor mechanical properties. Thus, incorporating advanced temperature monitoring systems can help ensure that the material is processed within its optimal range, ultimately enhancing the quality of the finished products and improving overall operational efficiency.

When designing molds for polycarbonate parts, it is crucial to consider the unique properties of the material. Polycarbonate is known for its strength, transparency, and ability to withstand high temperatures, making it an excellent choice for various applications. The design process should focus on maximizing the material's benefits while minimizing potential issues such as warping or cracking during the cooling phase. Implementing features like uniform wall thickness and appropriate draft angles can enhance the mold’s performance and ensure efficient material flow during injection.
Another key element in designing effective molds is the incorporation of advanced cooling channels. Proper temperature control is essential to prevent defects and maintain the integrity of the polycarbonate components. Cooling channels should be strategically placed to provide consistent cooling throughout the mold, helping to reduce cycle times and improve overall production efficiency. Additionally, utilizing time-tested techniques such as venting can alleviate trapped air, further enhancing the quality of the final product. By focusing on these design principles, manufacturers can achieve optimal results in polycarbonate injection molding.
When it comes to successful polycarbonate injection molding, controlling temperature and pressure is paramount. According to industry reports, maintaining optimal melt temperatures between 220°C and 250°C is crucial for achieving consistent material flow and minimizing defects. Too high a temperature can lead to thermal degradation of polycarbonate, while too low can result in incomplete filling of the mold.
Tip 1: Monitor the barrel temperature closely. To ensure a uniform melt, regular calibration of the barrel heating zones can prevent fluctuations that might affect the quality of the final product. Utilize advanced temperature control systems that provide real-time feedback to achieve precise adjustments.
Tip 2: Manage injection pressure diligently. Studies indicate that optimal injection pressures should typically range from 800 to 1,200 bar, depending on the specific application and part geometry. Applying excessive pressure can cause flash or even damage the mold, while insufficient pressure may lead to short shots. Incorporating pressure transducers during the manufacturing process can provide meaningful insights for adjustments.
Moreover, maintaining a stable cooling system throughout the cycle can enhance the overall quality, promoting a uniform solidification rate that further ensures dimensional accuracy. Recognizing and implementing these temperature and pressure controls can significantly improve the efficiency and quality of polycarbonate injection molding processes, ultimately leading to reduced cycle times and better product performance.
This chart illustrates the optimal temperature and pressure settings for polycarbonate injection molding, as well as common mistakes made in the process. The first dataset represents the ideal conditions for successful molding, while the second dataset highlights the extremes often encountered that can lead to defects.
Implementing quality control measures in polycarbonate production is crucial for ensuring the integrity and performance of the final products. One of the first steps in establishing an effective quality control system is to develop precise material specifications. Monitoring the raw materials used in polycarbonate injection molding can significantly reduce defects in the finished items. Regular testing for properties such as clarity, impact resistance, and thermal stability is essential. This quality assurance process should occur at multiple stages, from material selection to the final product evaluation.
Another vital aspect of quality control is the implementation of process monitoring techniques during the injection molding cycle. Utilizing real-time data collection tools can help in identifying variations in temperature, pressure, and cooling times that could lead to compromised product quality. Automated systems can detect these discrepancies early, allowing for immediate adjustments to be made. Regular maintenance and calibration of the injection molding machines also play a pivotal role in achieving consistent output quality, thereby enhancing overall efficiency and reducing waste. These proactive approaches ensure that the final polycarbonate products not only meet but exceed the desired quality standards.
| Tip # | Quality Control Measure | Purpose | Implementation Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Material Inspection | Ensure quality of raw polycarbonate | Conduct tests on incoming materials |
| 2 | Temperature Control | Prevent warping and defects | Monitor machine settings and adjust as necessary |
| 3 | Pressure Monitoring | Ensure optimal fill and minimize defects | Use pressure sensors to gauge levels |
| 4 | Cooling Time Optimization | Enhance cycle time and reduce defects | Adjust cooling rates based on part complexity |
| 5 | Visual Inspection | Identify surface flaws | Conduct regular inspections of finished parts |
| 6 | Dimensional Checks | Ensure parts meet specifications | Use calipers and gauges for accurate measurements |
| 7 | Load Testing | Confirm durability and strength | Test parts under stress to check performance |
| 8 | Cleanliness Standards | Prevent contamination in production | Establish clean room protocols |
| 9 | Shear Force Evaluation | Assess material performance under stress | Conduct shear tests on samples |
| 10 | Process Audits | Identify and resolve process inefficiencies | Regularly review procedures and outcomes |





880 W 9th Street
Upland, California 91786
884 W 9th Street
Upland, California 91786
886 W 9th Street
Upland, California 91786
884 W 9th Street
Upland, California 91786