Injection mold design is a critical component in the manufacturing process, playing a pivotal role in determining the quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of plastic products. Mastering this art involves understanding the nuances of designing molds that not only meet specifications but also optimize production cycles. As industries continually demand higher precision and faster turnaround times, the ability to create effective injection molds becomes a competitive advantage.
In this exploration of injection mold design, we will delve into key strategies and techniques that contribute to successful mold development. From material selection to cooling system optimization, each aspect of the design process impacts the final product's performance. With an emphasis on practical tips and industry insights, this guide aims to equip designers and engineers with the knowledge needed to enhance their skills in injection mold design, ensuring they can tackle challenges and innovate in their projects. By mastering these fundamentals, professionals can achieve remarkable results that elevate product quality while reducing production costs.
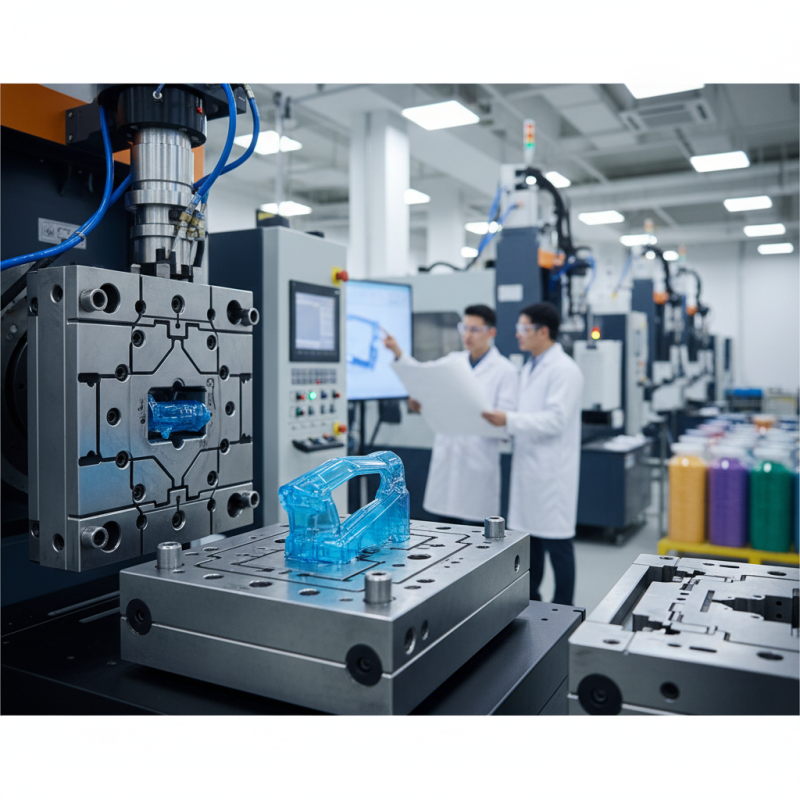

Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process that transforms plastic materials into various final products. By understanding the fundamental principles of injection molding, designers can create efficient molds that result in high-quality components. The process begins with melting thermoplastic pellets, which are then injected under high pressure into a carefully designed mold cavity. This allows for intricate designs and high precision, making it suitable for complex geometric shapes used across various industries, including automotive, consumer goods, and medical devices.
In addition to its versatility, injection molding also offers significant advantages in terms of production speed and cost-effectiveness. Once the mold is created, it can be used repeatedly, allowing for the mass production of parts with minimal variation. Understanding the different types of injection molding, such as multi-shot and gas-assisted molding, broadens the range of applications and can lead to innovative product designs that meet specific market demands. Mastery of injection mold design not only involves a firm grasp of these basic concepts but also requires ongoing learning about advancements in materials and technology to stay competitive in the field.
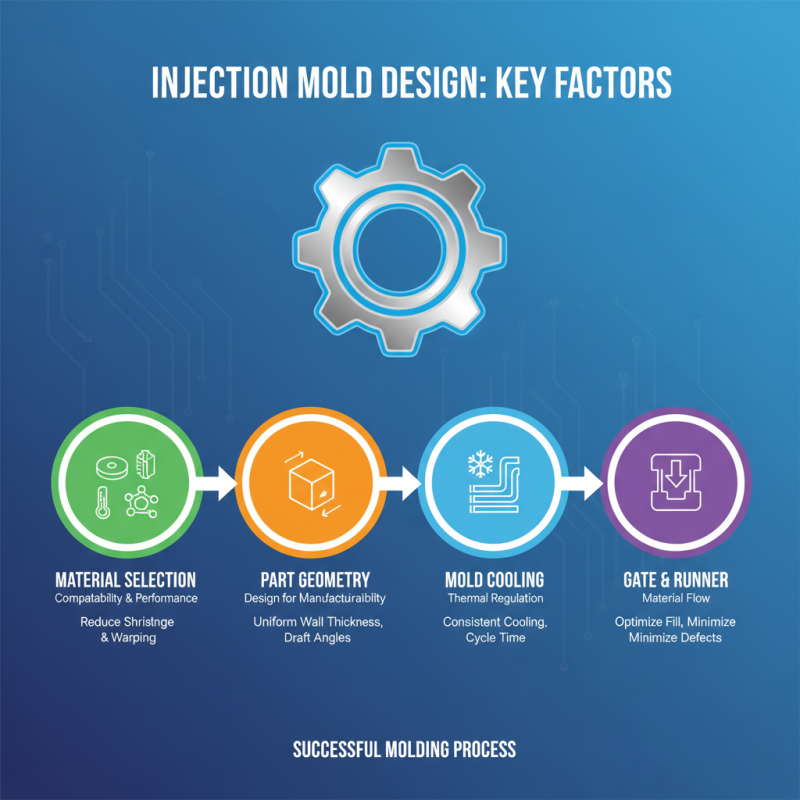
When it comes to injection mold design, several key factors influence the overall success of the process. One of the most critical elements is understanding material selection. The chosen materials must not only meet the mechanical and thermal requirements of the product but also be compatible with the molding process. Different plastics may behave differently under heat and pressure, making it crucial to choose materials that reduce shrinkage, warping, or other issues that can arise during production.
Another important consideration is the mold design itself, which encompasses the complexity of the part geometry and the overall mold structure. A well-designed mold can streamline the manufacturing process and minimize defects. Factors such as draft angles, wall thickness, and the placement of gates and vents play a significant role in ensuring an efficient cycle time and high-quality output. Additionally, incorporating cooling channels within the mold can enhance temperature control, leading to better part consistency and reduced cycle times.
Lastly, collaboration among engineering teams throughout the design phase is essential. Open communication between designers, engineers, and production teams fosters a holistic understanding of the project, allowing for innovative solutions to arise. By considering these factors, designers can significantly enhance their chances of successful injection mold design, providing efficient production workflows and high-quality end products.

When it comes to injection mold design, material selection is one of the most critical aspects that can significantly impact the overall success of the final product. Choosing the right material not only affects the performance and durability of the molded part but also influences production efficiency and cost-effectiveness. According to a report by the American Plastics Council, over 30% of production failures in injection molding projects can be attributed to inappropriate material choice. Therefore, understanding the specific properties and applications of various materials is essential for achieving optimal results.
In the context of material selection, factors such as mechanical properties, thermal stability, and compatibility with the intended application must be taken into account. For instance, engineering plastics like spandex or polycarbonate are often selected for their superior strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to heat, making them ideal for automotive and medical applications. A study by Freedonia Group indicates that the demand for engineered thermoplastics is projected to grow at an annual rate of 4.5%, highlighting the importance of innovative materials in injection molding. Furthermore, sustainability considerations are gaining traction, with a growing emphasis on biodegradable and recycled materials. This shift not only helps manufacturers meet regulatory standards but also caters to a more environmentally conscious consumer base.
In summary, careful consideration of material properties and emerging trends can lead to significant improvements in the injection molding process. By leveraging comprehensive data and staying informed on industry advancements, designers can enhance their projects' durability, functionality, and market competitiveness.
Optimizing mold geometry is crucial for achieving efficiency in injection mold design. One key aspect to consider is the flow path of the molten material. A well-designed flow path minimizes resistance and enhances the uniformity of material distribution, which ultimately leads to better part quality. Designers should aim for a balanced fill, ensuring that all cavities fill simultaneously to avoid issues like warping, sink marks, or visible seams. Utilizing advanced simulation software can help analyze flow patterns and identify potential bottlenecks early in the design phase.
Additionally, the design of the core and cavity should prioritize easy part removal while maintaining precision. Incorporating features such as draft angles and appropriate radii can significantly reduce the risk of damage during ejection. It is also essential to account for thermal considerations in mold design, as proper heat distribution affects cycle times and final product integrity. By integrating efficient cooling channels, designers can enhance the thermal management of the mold, leading to reduced cycle times and improved overall productivity in the manufacturing process.
Balancing these design elements can greatly enhance the efficiency of injection molding operations.
Testing and iterating injection mold designs are crucial steps in ensuring functionality and manufacturability. The first phase of testing involves analyzing the initial mold prototypes against detailed specifications. This can include a thorough inspection of materials used, dimensional accuracy, and the overall design’s compatibility with the intended manufacturing processes. Utilizing advanced simulation software can also help identify potential issues before physical production begins, allowing for adjustments in the design to enhance performance and reduce costs.
Once initial tests are completed, it is essential to engage in multiple rounds of iteration. Each iteration should address any shortcomings identified in the previous designs. Collecting feedback from production runs, such as cycle times and defects, provides valuable insight. This data-driven approach enables designers to make informed decisions, refining features like cooling channels or gate locations to optimize the mold’s efficiency. Continuous improvement through iterative testing not only leads to a more robust mold but also enhances the final product's quality and reduces time-to-market.






880 W 9th Street
Upland, California 91786
884 W 9th Street
Upland, California 91786
886 W 9th Street
Upland, California 91786
884 W 9th Street
Upland, California 91786